
 Loading...
Loading...
All about the Ethereum Merge, what nobody tells you
In a few hours, starting on September 15, 2022, the migration process also known as "merge" of the Ethereum network will begin, whose protocol will change from "Proof of Work" to "Proof of Stake", or at least, that's what everyone says. But in reality there are details that we will delve into in this article, in addition to mentioning some myths that are discussed about this update.
Indice
- 1. Introduction
- 2. The shareholders of the Ethereum network
- 3. What does all this have to do with NFTs?
- 4. About the update name
- 5. Ethereum, the upgrade of the network in 3 phases
- 6. Phase (1) – “The Beacon Change”, the staking simulation on the Ethereum network
- 7. Phase (2) – “The Merge”, debunking the myths of low costs and high speed of transactions
- 8. Phase (3) – “Sharding”, it will really change everything for the user experience
- 9. Ethereum vs. Polkadot
- 10. Investment opportunity?
Introduction
Before continuing, we suggest reading our article All about the Ethereum network, Polygon, Gas Fee and NFT to understand how the network worked until this update and to understand a little more about what we will write next.
Here we will mention everything you need to know, what these new changes imply, what the implementation phases are, what the risks are, the myths around this update, that is, everything you need to know about the new Ethereum "Proof of Stake”.
To understand a little what is coming, we remember the meaning of some terms that will be used below:
- Blockchain or Network: refers to the same thing, for example the Ethereum network is the same as the Ethereum blockchain
- PoW: communication protocol “Proof of Work” is an old protocol that is currently maintained by the Bitcoin and Ethereum network. This protocol requires the data mining process, where the so-called "miners" make their computers available to build digital blocks. This process consumes a lot of energy around the world and is very expensive.
- PoS: communication protocol "Proof of Stake" is a modern protocol that networks such as Polkadot, Solana and Cardano are already implementing. It is a consensus protocol created to replace the well-known PoW, providing better security, scalability, speed and low costs to the networks that implement it. It does not need computers or data mining making it energetically friendly. It basically works through cryptocurrency staking.
- Staking: It consists of a process of blocking cryptocurrencies or tokens in a wallet for a certain period of time to participate in the validation of transactions.
The shareholders of the Ethereum network
Later we will expand on the phases of this update, we anticipate that there are still a few years to go before the entire process ends and the benefits can be obtained in the user experience, but we do not want to miss this important detail that will come with the renewed Ethereum.
For the holders of the Ethereum cryptocurrency or of NFTs minted under this network, it is a great advantage that the PoW aborts and becomes PoS, since they will become the true shareholders of the network because if they make the decision to leave their ETH in staking they will be participating in the consensus of the transactions by making their cryptocurrencies available to a validator node and charging commissions for the mere fact of leaving their tokens immobilized, while when it worked with the PoW protocol, the shareholders were the miners who made their equipment available to build the chain of digital blocks charging a commission attributing a percentage of the network.
For the reasons mentioned in the PoW, the holders had a cryptocurrency that did not represent the value of the network, while in the PoS the cryptocurrency represents validation power within the network, therefore its value (not its price) is higher than in the old network.
What does all this have to do with NFTs?
At this point you will be wondering what this has to do with the world of NFTs, the answer is a lot, since most of the NFTs that are marketed are created on the Ethereum network and each transaction that we need to carry out with our NFTs, either creation, transfer, purchase or sale writes a chain of digital blocks on this network, which implies the consumption of resources and giving an amount called "Gas Fee" as network commissions.
As we will see later, when all the phases of this update are completed, we will surely observe very low prices of "Gas Fee" and a much lighter transaction speed, which will save and speed up creating and trading with our minted NFTs in the Ethereum network, but what no one tells you is that there is still a long way to go.
About the update name
The first thing we need to understand about the "Ethereum 2.0" upgrade is that it is no longer called "Ethereum 2.0" because it is actually a protocol upgrade process, a protocol gives functionality to the network, when the protocol changes the processes that make the network work but the network is the same, it is still the Ethereum network, the digital blocks are the same, everything written on this network remains intact, what changes is the way they are read and generate that data.
The Ethereum Foundation had decided to give it that name but this generated a lot of confusion since many believed that it was changing from an old network to a new network and as we have explained this is not the case, but that the change will occur in the communication protocol that makes operate the network. Therefore all NFTs and ETH cryptocurrencies remain intact and you do not have to change them or do anything with them. Around this confusion many scammers have created fake tokens called Ethereum 2.0 trying to sell them to the community as an investment opportunity making them believe that it was the new Ethereum. But none of this existed as the upgrade never involved a new token or cryptocurrency. Therefore the Ethereum Foundation decided that this update would no longer be called Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum, the upgrade of the network in 3 phases
The update of the network is a process that basically takes place in 3 phases, of which the first phase called "The Beacon Change" has already concluded, the "Merge" that will begin shortly is the second phase and much later the third phase called "Sharding" on which we will delve further later. The update process is similar to a roadmap, but there are still a few years to go completely.
Phase (1) – “The Beacon Change”, the staking simulation on the Ethereum network
“The Beacon Change” was implemented on December 1, 2020 but did not change the user experience or layer 1 of the Ethereum PoW network. “The Beacon Change” is another chain of blocks separate from the Ethereum network that works only as a consensus chain, that is, it does not allow transactions to be executed nor does it allow the storage or execution of smart contracts (where NFTs come into play) but only consists of a consensus layer where you can "Stake" the Ethereum network.
Let us remember that “Staking” is a PoS own action to which it is intended to migrate. But then how can you stake on the Ethereum network if it still works with the PoW protocol? "The Beacon Change" specifically simulates a staking but in reality it is not like that, but technically they are allowed to "burn" the Ethereum tokens by sending those to a wallet called "burn wallet" where they are kept "dead". At the same time, these tokens are minted or created in the new Beacon Change network that works under the PoS protocol and there those are staked, so that it seems that Ethereum is being staked but technically that never happens, rather It is a process executed in block simulating staking since it does not exist in a PoW network.
Surely you are wondering which is the "burn wallet" where all these Ethereum tokens that are unused because they have been minted in the new Beacon Change layer will end up. Here we show it to you!
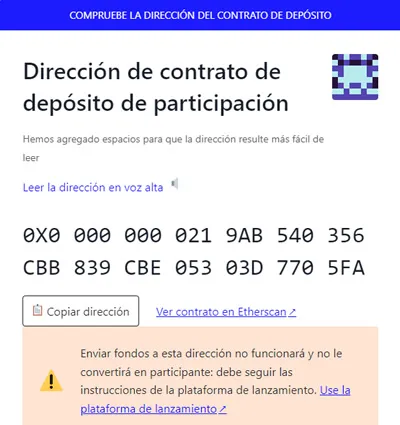
Link to see the address of the wallet where the ETH tokens remain in disuse, later minted in the Beacon Change layer: https://ethereum.org/en/staking/deposit-contract
The wallet address is 0x00000000219ab540356c BB839Cbe05303d7705Fa
ALERT: Do not deposit ETH in this wallet as it will cause the loss of your funds, if you want to participate in staking you must follow the steps indicated in the provided URL
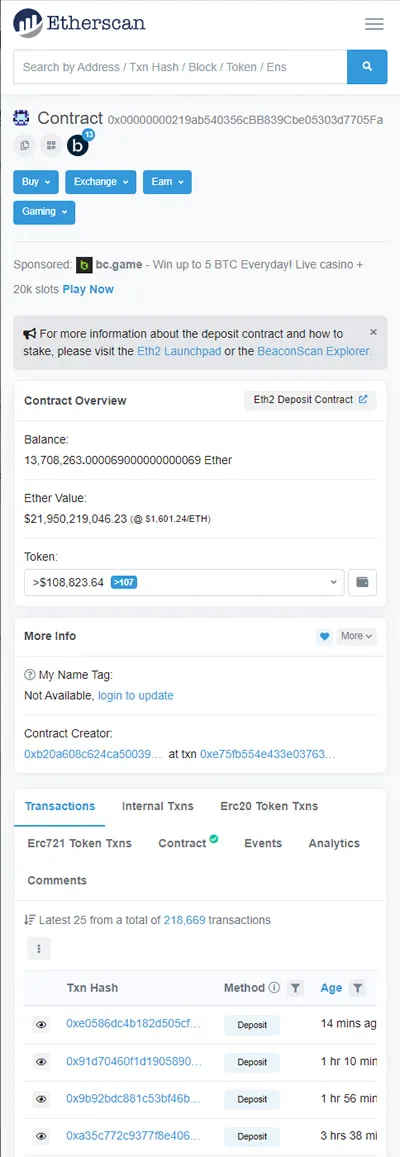
Link to see the contract in Etherscan: https://etherscan.io/address/ 0x00000000219ab540356c BB839Cbe05303d7705Fa
As can be seen in the capture at the time of writing the article, the balance of this wallet is 13,708,263 Ethereum, the equivalent of approximately 21 billion US dollars of disused tokens that were later minted on the layer “The Beacon change”. In other words, simulated ETH tokens staking on PoW, the prelude to PoS.
In short, "The Beacon Change" is a network that they have created in parallel allowing Ethereum to be burned in the PoW and staked in this new network. The reason the Ethereum Foundation built this mechanism was to make it possible to progressively test and build the new Ethereum PoS network that will ultimately replace the current PoW-powered one. Let us remember that “The Beacon Change” does not allow transactions to be executed nor does it allow the storage or execution of smart contracts, it only functions as a passive network that serves to stake the ethereum token, fulfilling a single role as a consensus chain.
Phase (2) – “The Merge”, debunking the myths of low costs and high speed of transactions
As we mentioned at the beginning, this phase will begin in a few hours, between September 15 and 18, 2022. The “Merge” consists of definitively ending the network that works under the “Proof of Work” (PoW) protocol and merging it with the “Proof of Stake” (PoS) network, that is, merging it with the Beacon Change that was implemented in phase (1). From the moment the merge or union of both networks is executed, there will only be one single network and everything will start to work under the PoS protocol. Therefore, the Beacon Change that before the merge could not execute transactions nor did it allow storing or executing smart contracts, from this phase (2) it will be able to do so.
Undoubtedly, the merge phase is the most critical point of all, since it involves the merger of the two blockchains or networks that worked until now, the ethereum PoW with the Beacon Change PoS. In other words, both will come together and form a single block chain or network that, as we said at the beginning, will continue, being called Ethereum.
As a result of the merge, several myths and misunderstandings have arisen about the operation of the network. Basically it is said that the network will drastically lower its costs per transaction represented in the "Gas Fee" and will also become a super scalable network executing transactions at high speeds. In truth none of that will happen at this phase (2). For the Ethereum Foundation, the sole objective of the merger is to get the network to start working with the PoS protocol, seeking to consume less energy and be more environmentally friendly. And this is because the PoW protocol whose functionality was counterproductive in this sense is abandoned, we have explained it at the beginning of the article.
The Ethereum Foundation explains to us that the "Gas Fee" is a product between the demand of the network and the capacity of the network. What is clear is that the capacity of the network will not increase with the merge and that the demand will remain the same, therefore there is no reason for the "Gas Fee" to be reduced. What the merge does is change the protocol that the network will work with, from PoW to PoS. Transactions will not be faster either, perhaps speeds will improve as little as 10%, no more, as new blocks of digital data could be proposed less frequently.. They also explain to us that the Ethereum staking, the simulated staking that we mentioned in phase (1), will not be able to be undone with this update, but that we will have to wait for a future update that will be given in phase (3).
In short, from the merger with the PoS, the Ethereum network will not have the scalability, speed, or low commissions in "Gas Fee" that everyone is waiting for, it does not modify the user experience.
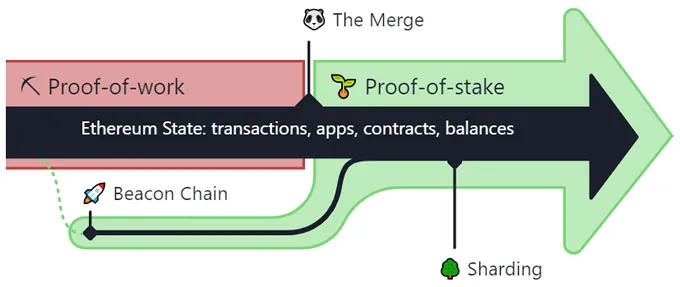
Source: ethereum.org - In the graph we clearly see how each of the phases of the Ethereum network update are represented.
There is a possibility of a fork in the Ethereum network where both protocols coexist during the merge due to the fact that many data miners are reluctant to abandon mining and continue doing so, but in this hypothetical case, it could not last long according to the Ethereum Foundation.
For the reasons that we have explained at the beginning, a point to highlight already in the PoS merge phase is that the users who own the ETH tokens become the true shareholders of the network, ceasing to be the data miners.
Phase (3) – “Sharding”, it will really change everything for the user experience
After completing this last phase of the Ethereum network update, which still does not have a pre-established date, it will be when everything will really change for the user experience. In other words, "Sharding" will bring low commissions or "Gas Fee", speed and practically infinite scalability. The "Sharding" will be executed in two phases or sub-stages. But it should be noted that improvements and new technologies are renewed daily, therefore when phase (3) is executed, the planning times and the sharding phases may change. It is estimated that this process may take a few more years.
In the first phase, basically, sharding will allow the distribution of data storage in several sub-networks that will be attached to the Ethereum network as a second layer, which will decompress the current network, opening the door to the aforementioned benefits for the user experience. Currently these second layers also called roll-ups already exist, such as "Arbitrum" and "Optimism" but they are not yet coupled but have managed in the Ethereum ecosystem to be able to develop. Sharding will make Ethereum itself join the roll-ups and embrace them within its ecosystem, giving them shared security and optimal development so that they can store data and execute code.
One of the biggest problems that a blockchain like the Ethereum network has is data storage, if this technology were to start being used on a massive level, the ecosystem would grow at exponential levels, so it would become saturated and its weight would be exceeded to the point that It could be compared to a giant with lead feet, making transactions slower and slower, making it unfeasible.
To avoid these consequences, what is intended with this update is that the ethereum network is layer 1, having the ability to couple the roll-ups that in the future will be called "sard-chains". These sard-chains are basically second layer solutions that will be stacked on top of the Ethereum network by bundling transaction packets and including them as a single transaction within layer 1 of the Ethereum network. The goal is for sard-chains to store information and execute code in such a way that there can be information that is stored in the sard-chains but not in layer 1 of Ethereum.
With this architecture and functionality, the weight of the blockchain is distributed in several different chains, enabling a lighter and less expensive network in transaction fees. It is within these coupled sard-chains that extremely low gas fees and fast transactions will be experienced, not in layer 1 of Ethereum. In short, the roll-ups or sard-chains will distribute the weight of the Ethereum blockchain between different sub-blockchains so that the scalability is much higher.
The second phase of this phase 3 will be when the sard-chains can execute their own code and generate their own smart contracts, literally becoming a replica of layer 1, that is, the difference between layer 1 and layer 2 composed of the sard-chains will be null. Layer 1 of Ethereum will not change, it will continue to be heavy and slow, but by incorporating sard-chains as replicas of layer 1 having all the attributions of the same, all operations will be executed in these second layers, light and with costs very low. Something similar is already happening with the Polygon network, which works independently of the Ethereum network but emulates what these sard-chains will do in the future.
Layer 1 of the ethereum network will secure the entire ecosystem, but transactions will be executed on sard-chains. At this point there will be what the Ethereum Foundation calls a scalable network with 100 thousand transactions per second, but not in layer 1 of Ethereum, but distributed throughout all the coupled sard-chains as the second layer of the network.
Ethereum vs. Polkadot
All the technology and functionality that we have explained previously where the Ethereum network is in the process of migration, which still has a few years to materialize definitively, already works very efficiently on the Polkadot blockchain. Even Polkadot allows sard-chains to communicate with each other, while Ethereum will have to achieve this in later phases.
In other words Ethereum is copying Polkadot technology, the difference is the size of the community. While Ethereum has an exponentially larger community than Polkadot, the latter is technologically “light years” ahead. So a competition of giants is taking place to see who can first meet the 2 conditions: a network with the technology we describe and at the same time have superiority in users.
Ethereum is far ahead at the user level and Polkadot is far ahead at the technology level. Surely in the coming years there will be a race to achieve interoperability, scalability, lower commissions, etc. We can speculate that in the future both networks will connect with each other in a collaborative way and not so much that the matter is oriented towards their competing with each other.
Investment opportunity?
Studying the projects that apply as "sard-chains" of the Ethereum network could be an investment opportunity, but you have to be careful because just as successful projects can appear, projects that fail in the attempt can also appear. That is why we always have to investigate each project, learn about the subject and draw our own conclusions. This opportunity is not obvious to everyone, it will only be so when the sharding phase is over and when the tokens associated with these projects have already skyrocketed in their market values. But for that it is estimated that 2 or 3 years are missing.
NFT Trends
Your contribution is essential to keep our site online and support content creation.
We will verify the sending of the funds. This may take us a while.














